Filed under: Analysis, Northeast, Police, White Supremacy
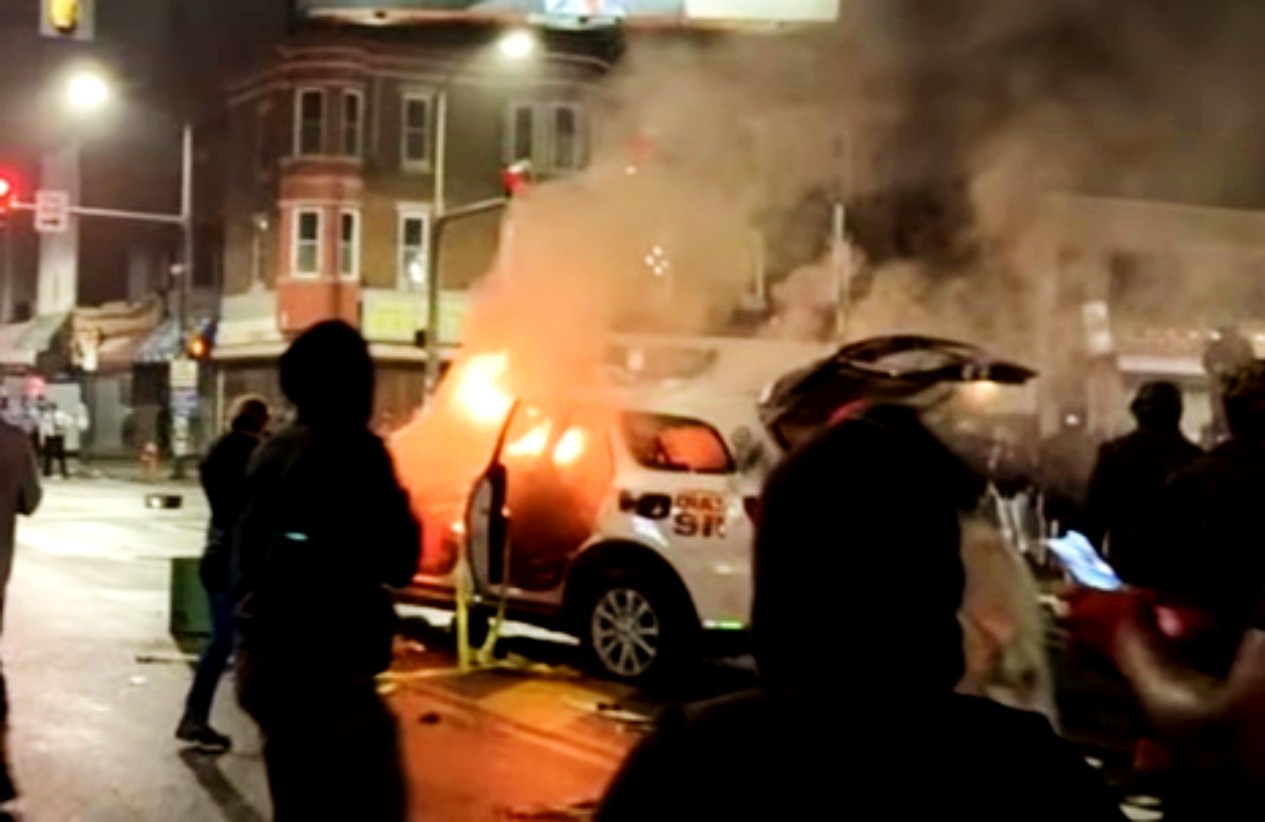
The US saw some of the largest riots and protests in its history this year in response to police murder of black people. Yet there has been scant attention paid to the innovations in struggle specific to these rebellions. Shemon & Arturo take another look at the phenomenon of car-looting and argue that this tactic is inseparable from black liberation. Originally published to Mute.
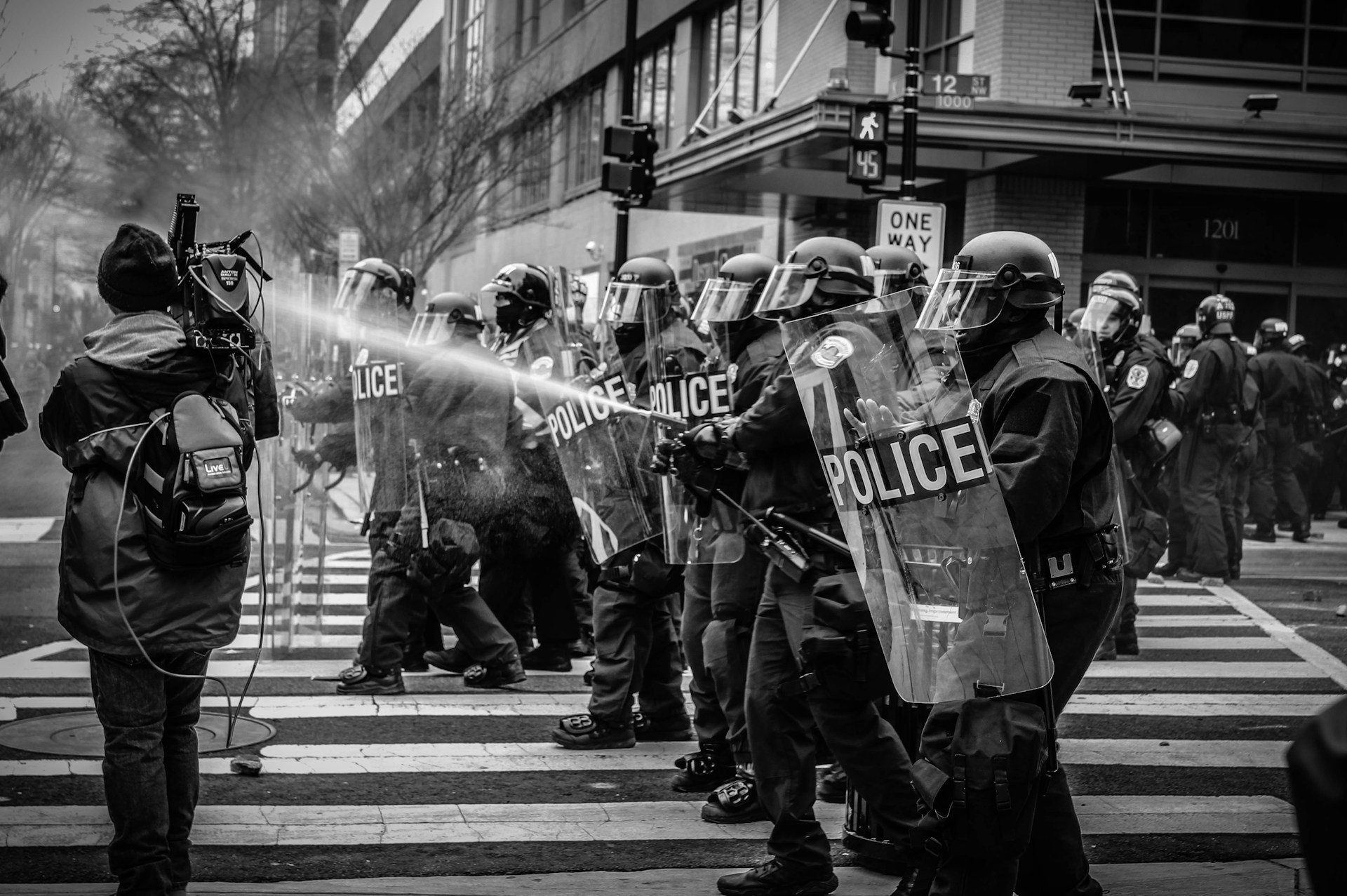
Glass shatters. Thick plumes of dark black smoke pour out of a burning police car stalled in the middle of 52nd street. Another black man shot dead by the police. Another rebellion in defense of basic human dignity. ‘Sir, it’s chaos!,’ one of the officers yells into his radio as they retreat under a barrage of rocks, bottles, bricks. ‘Stop throwing shit!,’ an older black man on a bullhorn yells, but the young black militants keep throwing projectiles anyway. The police, outnumbered by the hundreds, can only watch from a distance as people begin to loot stores all along the ave. The cops concentrate on blocking off major intersections.
While sitting in a traffic jam, waiting for the red light to turn green, a car breaks whatever is left of the law and speeds away. Time and speed do not obey red, yellow, or green here. This is no ordinary traffic jam. It is the traffic jam of black liberation, where looting by car is the art form developed in response to the murder of Walter Wallace Jr. by the Philadelphia Police.
All of a sudden a group of black teenagers pop out of a car and walk down the street, to an unknown destination. Cop cars zoom past them in a panic of sirens, red and blue lights flashing through the darkness, probably rushing to another 9-11 call about looters at a pharmacy, Footlocker, grocery store, or liquor store somewhere else. Across the street, a gas station is filled with cars of young black people hopping in and out, discussions taking place, and music blaring. It is part music festival, part pitstop, and part modern day proletarian council where young people discuss what to do next.
Philadelphia police arrested over 90 people at protests over the police killing of #WalterWallaceJr. On Tuesday, they were filmed beating some with batons.
1 activist said: "You cannot retrain hatred… They routinely get away with doing things to us, there's no accountability." pic.twitter.com/Cv6VEI8xIZ
— AJ+ (@ajplus) October 28, 2020
What happened in Ferguson as an impromptu practice has developed into an art in Philadelphia: the art of looting by car. In the United States, black proletarians are constantly refining and sharpening forms, tactics, and strategies of struggle.
In the official record, these activities will be recorded as crime. Joe Biden has already left his statement for all of posterity to see. Biden, like all politicians, spews the great lie of our society: black rioters are criminals. Riots have nothing to do with politics. But there could be nothing further from the truth. Black rioters are the creators of new forms of struggle, new visions of liberation, and new types of revolutionary organization. The accomplishments of the revolt in Philadelphia were powerful, liberating and simply beautiful. While pundits want to dismiss the riots as apolitical or criminal, it is the revolutionary activities of the black proletariat which constitute the actual form of politics that put radical change on the horizon.
Ignoring the Uprising
The main people who take the uprising seriously are the Right and a small layer of the ultra-left. For liberals and moderates the insurrectionary dimension of the uprising barely exists, since 93 percent of the protests have been baptized as peaceful. Using this statistical sleight of hand, liberalism transforms itself into an ally of black people, equating Black Lives Matter with respectable, non-violent, legal protest, while ignoring the remaining 7 percent of violent protests, i.e. the actual riots. Even socialists have stuck their heads in the sand when it comes to the tactical and strategic implications of the uprising. Everyone condemns racism and police brutality, but for all their claims of solidarity with black liberation, most leftists have fallen miserably short when it comes to actually participating in the riots that have swept this country. At best, most abstain from the insurrectionary aspects of the uprising altogether; at worst, they opportunistically leech off of it in order to build up their particular organizations, brands, and careers. Meanwhile, black proletarians are getting arrested and putting their bodies on the line in a battle of life and death.
At this point in the development of the struggle, any group that claims solidarity with black liberation, but has not been fighting the cops and rioting in the streets, or directly providing aid and support to such activities, is irrelevant. There are no excuses. We have met women, children, parents, elders, undocumented people, people in wheelchairs, on crutches, coming from all genders, abilities, and races imaginable, all throwing down in one way or another during street riots. For those who engage the police in battle, the time for words and social media posts are over. This kind of symbolic anti-racism and solidarity – which has been the bread and butter of liberals and leftists for decades now – has been exposed for the joke that it really is. Solidarity with the movement requires risking your skin. This is not an abstraction; this is exactly what black proletarians are doing.
And it is not only the white, Asian, indigenous, and latinx left that ignores the most dynamic and militant aspects of this uprising, it is also the major black intellectuals and radicals of our time. This should be no surprise, as a similar split occurred among radical intellectuals during World War I in the Second International and again in national liberation struggles during World War II and after.
For all the radical rhetoric of marxism, in terms of its actual deeds and practice, most of the radical left has accommodated itself to the status quo. The law has expanded in response to class conflicts and anti-racist struggles to the point that plenty of harmless forms of activism can be engaged in, but they are simply a new prison for activists and movements. Previous generations have won victories and expanded the law so that we can safely denounce wars, march almost anywhere we wish, and say whatever we want. This range of legality seems like a victory, but has also become a trap that leftist organizations treat as a principle. The fact of the matter is that leftist organizations are simply not prepared to deal with the illegal nature of the revolutionary struggles and politics that are taking place in the present moment. The black proletariat continues to show a practical commitment to fighting the police, setting fire to carceral infrastructure, and looting the commodities of this dying capitalist system. When these are the tactics of the proletariat in motion, what kind of organizational forms make sense?
#BREAKING OVERNIGHT: #Brooklyn protests turn destructive in wake of Philly police shooting death of #WalterWallaceJr@ADiLorenzoTV has the latest all morning: https://t.co/zJVUyKPg02 pic.twitter.com/eSUdXhp9Ok
— PIX11 News (@PIX11News) October 28, 2020
Organizational, tactical, and strategic clarity is emerging for the first time since the 1960s, but it is not coming from the left – it is coming from the practical initiatives and strategies of the black proletariat. Leftists run their mouths about organizational questions in abstract and antiquated terms, regurgitating a played out formula modeled on Russia or China that has been repeated ad nauseam for many decades now, but which has produced little more than sects and cults. They ignore the concrete forms of revolutionary organization that are already taking place in the uprising.
Revolutionary organizations are not built in the abstract, but are expressions of the real tactical and strategic challenges raised by the proletariat in the class struggle. The fundamental organizational question that revolutionaries face is how to contribute and relate to the uprising, specifically in terms of street fighting, looting, and other riot tactics. Those who are truly committed to revolution will have to push past the stale organizational forms of the past and begin to account for the diverse, illegal, and creative organizational forms that the black proletariat is developing in the present, the use of cars being one of the most innovative and effective tools in this emerging tactical repertoire.
It cannot be completely spontaneous that black proletarians went to Wal-Mart, looted it, and when the cops arrived, evaded them and went on to form caravans that targeted different shopping districts throughout the city. Much of the official prognosis of this moment is that the rioters are unorganized, lack direction, and leadership. In truth, the reality is that there’s a high degree of coordination and organization within the maelstrom of the riot. This should be obvious when caravans of looters swarm specific locations at the same time. To do so, people collectively decide on specific targets, coordinate movement to the target area, and often set up look outs who will warn everyone else when the police are coming.
New Dynamics, New Divisions
Organizations prove themselves in the battle of class conflict, often for specific purposes. In the case of Philadelphia, any organization had to deal with the dynamics of feet and tires. Most people destroyed property and looted stores in one manner or another by marching in the streets, and when the cops came along, they fought and evaded them on foot. But as the state has become more and more prepared for riots, prolonged street confrontations with the police have become more costly, and it has become harder to continue on foot. We first saw this in Chicago after the murder of Latrell Allen, where a caravan of cars looted the Magnificent Mile, and from there dispersed themselves throughout the city. This trend continued in Louisville with the Breonna Taylor protests in late September, where state preparation made an uprising in the city practically impossible. In response, people took to cars and spread the riots geographically by looting businesses throughout the city. This was a brilliant tactical and ultimately strategic innovation when facing the raw power of the state.
Car looting has clear advantages to looting on foot. There’s less peace policing, because there is not as much of an association with a specific geography, and what is often the same thing, a specific race. The most important aspect of car-looting, however, is that it disperses and exhausts the police forces. This strategy also creates a dynamic where those left on foot may find themselves in de facto police free zones, able to revel in freedom for extended periods of time, because the police are too busy trying to counter the looting caravans elsewhere. This is what happened in Philadelphia. The synergy of those on foot and those in cars creates a different geography and dynamic of struggle where police cars are racing from store to store trying to stop the roving bands of car looters, while those on foot find themselves pulling police resources in a different direction. There are simply too many rioters in different places and not enough police.
Looting by car is a strategic advancement, but the car is certainly not a perfect tool. The license plate is a huge security risk. With a few keystrokes police can use your license plate to look up your address and knock on your door. While this presents many dangers, what’s important to note is that many proles are finding ways to loot by car and not get caught regardless. Besides the risks that come with having a license plate, evading the police by car is oftentimes more dangerous and getting caught after a high speed chase is going to result in longer jail time.
Philadelphia enters into a second night of rebellion following the police killing of #WalterWallaceJr as people march in DC following the police killing of #KaronHylton. Militant marches in #NewYork and other cities also hitting the streets. pic.twitter.com/yzaAr366st
— It's Going Down (@IGD_News) October 28, 2020
Besides the security risks, the second problem is that you need a car in the first place, or at least need to know someone who has a car. While car ownership is widespread in the US, it is determined by race and class. According to a study from the University of California, ‘African Americans have the lowest car ownership of all racial and ethnic groups in the country, the researchers say, with 19 percent living in homes in which no one owns a car. That compares to 4.6 percent of whites in homes with no car, 13.7 percent of latinos, and 9.6 percent of the remaining groups combined.’ While not having your own car is probably not a total barrier, taking note of the unequal ownership of cars is important. At the same time, the fact that car-looting has so far been almost entirely black shows us the determination of black proletarians to use cars in the uprising.
The third concern is that the car simultaneously atomizes the struggle, where each car is a separate unit. While in a way, the car socializes small units of rioters, it does so in a very different manner than looting on foot. Each car is a ship unto itself. It’s not always clear if human beings are directly relating to one another or if it is the car as a commodity which emerges as the subject. This mask is torn off in the rush of doors opening, looters jumping in and out of cars. From the outside, however, car looting can be fairly mysterious. Drivers and passengers can hide behind tinted windows and it becomes difficult to engage them. Joining a random car caravan can invite suspicion, especially if the caravan is made up of friends who already know each other. New faces are correctly suspected. This is all very different from looting on foot, where there is much more of a social and collective atmosphere. Still, looting by car is almost impossible to do as an individual, and thus, entails its own kind of sociality.
If the initial division of the uprising was between legal and illegal protests, non-violent and violent protests, good and bad protesters, it is clear that another division has emerged: shoes versus tires. However, this division is not an obstacle to the struggle. Unlike previous divisions which reflected class and racial differences in the movement, this one emerges directly out of the tactical back and forth between the police and the black proletariat. This organic division arises in response to the maneuvers of the police, and therefore, reflects innovation and creativity, instead of containment and counterinsurgency.
New Geographies of Struggle
To understand car-looting is to catch a glimpse into the changing geography of struggle. The size of cities can give us a baseline reference point. Philadelphia is 134 square miles and Louisville 325 square miles. To put that in perspective, New York City is 302 square miles and Oakland is 78 square miles. This information gives us a sense of the specific size of the container we are dealing with, but if we want to grasp the full geographic dimensions of a city, there are particular infrastructures, densities, and social dynamics that determine why car-looting takes place where it does. In New York City, for example, looting by car was not a mass phenomenon. Why has looting by car happened in Chicago, Louisville and Philadelphia, but not NYC? The low car ownership rate (at about 50 percent), the high concentration of stores and people, coupled with an extensive subway system, all come together to militate against the use of cars in riots. This is not to say that some car looting did not take place, just that it was not the decisive element of the rebellion in NYC. But in cities like Louisville and Philadelphia, cars became major components of the uprising. Furthermore, if the initial phase of the uprising this summer was concentrated on the wealthiest portions of cities, in the fall the proletariat abandoned Market Street in Philly, and abandoned Jefferson Square Park in Louisville, and instead used cars to spread the rebellion throughout the city. Instead of fixating on territory in the way that activists tend to do, those who looted by car used the vastness of urban space to create a new territory of struggle. This is part of a qualitative development in the class struggle that still needs to be made sense of and accounted for.
A century ago it was factories which dotted the terrain of class struggle; today it is the shopping district, the cell phone store, the CVS, and the Apple store that reveals the new geography of struggle. Rioting and looting are a reflection of what capital looks like now: wealth in the form of commodities concentrated in key neighborhoods, often spread geographically throughout cities. While these commodities are not the means of production, they certainly represent a vast collection of wealth just waiting for proletarians to expropriate. The looting of Wal-Mart is an excellent example of this. Here capital has brought together a vast assemblage of commodities which proletarians usually have to pay for. The looting of Wal-Mart on the night of 27 October was the reaction of people who are forced to live and work alongside this hyper concentration of commodities. While precise data is not available of what kind of jobs rioters hold, an educated guess is that if they hold jobs at all, they are most likely in low-wage service sector jobs with little structural power to strike. Instead of critiquing rioters, then, it makes more sense to ask why proletarians in the United States are rioting more than they’re striking.
Weapons and Ethics
We’ve seen right-wingers use cars to attack protestors. The big pick-up truck and the Trump waving sedan has become a weapon to intimidate, injure, and kill BLM protestors. In response, many activists formed their own car brigades for surrounding protests and blocking right-wingers from ramming protestors with their cars. While this has been an important development, another and much less noticed development has been the growing use of cars for looting. This turn in tactics raises more general questions about the tools we use, how we use them, and how these tools relate to liberation.
Reflecting on the use of guns in his recent text ‘Weapons and Ethics‘, Adrian Wohlleben tells us that the weapons we use and how we use them powerfully impact our struggles. We should be attuned to how specific weapons might increase collective power and mass participation, while others might limit them. Wohlleben throws some cold water on any romanticism about guns, and equally important, pushes us to think about how the use of guns changes the terrain of struggle. Most crucially, Wohlleben demonstrates a commitment to keeping the movement mass based and militant at the same time. Weapons and Ethics asks: ‘How does our use of weapons work behind our backs to define the meaning and limits of our power? How does this choice affect and configure who feels able to join us, and even what we think of as ‘winning’? How can we make this choice explicit to ourselves?’ While there is much to agree with here, we can also critique Wohlleben for not navigating the precise history of how guns have been used for black liberation. While it was not Wohlleben’s purpose to do such an analysis, in the context of the George Floyd uprising, and a potential civil war, it is clearly a task we must turn our attention to. And like guns, there is an ethics around cars, but one that is radically different. How do Wohlleben’s questions square with the use of cars for black liberation?
We usually do not think of cars as weapons, but they have been for some time. The car bomb has been used for decades. Considering how widespread cars are in this country, it is not inconceivable that they will be used in such a manner as struggle escalates. While we’ve seen cops and right-wingers use cars against BLM protesters, there were also several incidents in Philadelphia in which cars were used as weapons against the police during the riots. Police were attacked with cars during the Walter Wallace Rebellion, during the George Floyd Uprising back in May, and also in NYC.
After guns, cars are probably the most American of products. The very origin story of the car is inseparable from the rise of the United States as an industrial and global power. And while many on the left correctly criticize cars as climate destroying machines, there is an alternative history of the car that we must pay attention to. The car, commonly understood as one of the defining symbols of American capitalism, has been turned on its head, and repurposed as a weapon of black liberation.
From Ferguson to Philly
The use of cars for black liberation is not new. The Montgomery Bus Boycott in 1955-56 is perhaps the most famous example. Civil rights activists, particularly black women who were domestic workers, organized an alternative public transportation system based on cars in order to boycott the segregation of the buses in Montgomery, Alabama. This history provides valuable lessons for our current moment, especially when it comes to the question of social reproduction. This movement was a large-scale challenge to white supremacy. However, cars were not exactly used as weapons of struggle, as they are today. The manner in which cars are currently being used in riots reflects an escalation of the class struggle. If we begin with Ferguson, we see cars being used as getaway vehicles, as barriers to create police free zones, and as shields to fire at cops. But cars in Ferguson were not used for the purposes of looting. The Ferguson uprising did not spread geographically in response to the police. Instead spaces were defended around several sites in Ferguson, most importantly the QT and Canfield and West Florissant. Compared to the 2010s, the riots happening today have escalated in intensity and expanded in geography. The caravan of looters is probably the best example of this.
West Philadelphia.#phillyprotests #WalterWallaceJr pic.twitter.com/lMHnN3jZZh
— Dina Nassar (@dinathedoc) October 28, 2020
Dozens of gas guzzling monsters roaring down the streets, tires screeching, tinted windows – this is the caravan of black liberation. This phenomenon is an important aspect of the moving wave of mass struggles. It can be understood through the framework of Rosa Luxemburg’s great text The Mass Strike. While many anti-capitalists agree with Luxemburg today, it was a controversial argument that she was making at the time. Luxemburg challenged the widely held conception of how a post-capitalist would come about in the 2nd International: a peaceful evolution won by the vote. Instead, she demonstrated that the strike waves rolling through Eastern Europe were the key to revolution. While it would be foolish to claim that car-looting alone will get us to a new world, it is one response of the black proletariat to a variety of tactical, strategic, and political economic developments of our time. How this strategy will connect to the wider revolutionary current is not fully clear, but it is communistic in the sense of its mass nature and its attack on the commodity form.
What we see from Ferguson to Philadelphia is the growing use of the car as a weapon of mass struggle. In Ferguson cars were used for defensive purposes, while in Chicago, Louisville, Philadelphia and elsewhere cars were used for offensive purposes: for looting, for attacking police, and for spreading the geography of the uprising. We should expect cars to continue to play an important role as riots continue to unfold and the uprising potentially mutates into other forms of mass struggle: blockades, strikes, and occupations. Undoubtedly, the state will respond with new forms of surveillance and repression, but how it will do that is unclear. In the meantime, black proletarians will probably take advantage of the state’s lack of capacity to deal with widespread car-looting.
Conclusion
Over the summer comrades and CrimethInc. published an exciting text, ‘Tools and Tactics in the Portland Protests‘, which showed the creativity and dynamics of the Portland protests. Each move by the federal agents forced protestors to develop a counter move, creating a back and forth dynamic that defines the tactical pulse of any mass struggle. While the street tactics of the Portland protests are familiar to many people across the country, making sense of car-looting is much more difficult if you aren’t part of the caravans of looters. But none of the obscurity of car-looting should stop us from recognizing that cars are inseparable from a strategy of black liberation. While it can be difficult to forge bonds with car caravans, this is a developing form of mass struggle where many of the divisions of our society might be broken if non-black proletarians can figure out how to participate.





